Today, we will take a look into hashing and encryption techniques to save passwords in the DB in an encrypted way instead of a plain-text.As there are many encoding mechanism supported by spring, We will be using Bcrypt encoder mechanism provide by spring security as it is the best encoder available.In the mean time, we will be using Spring boot to avoid common configurations.Of course, there are also other encoding mechanism like MD5PasswordEncoder and ShaPasswordEncoder but these encoders are already deprecated.
What is Bcrypt Encoding
As per wiki, bcrypt is a password hashing function designed by Niels Provos and David Mazières, based on the Blowfish cipher. Bcrypt uses adaptive hash algorithm to store password.BCrypt internally generates a random salt while encoding passwords and hence it is obvious to get different encoded results for the same string.But one common thing is that everytime it generates a String of length 60.
You can also take a look into this Online Bcrypt Tool to know how bcrypt works.
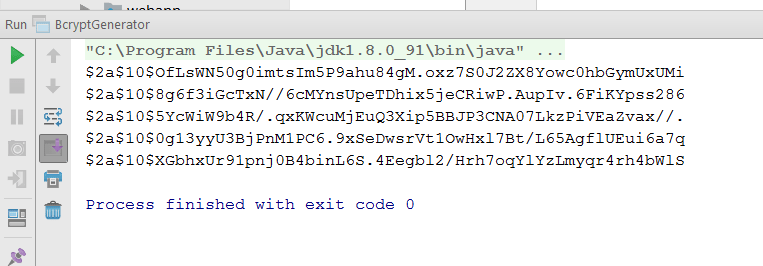
First of all let us give a look into the program that will Bcrypt any given password.We will be storing the first result to the DB.
package com.devglan.config; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; public class BcryptGenerator { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; while (i < 5) { String password = "password"; BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); String hashedPassword = passwordEncoder.encode(password); System.out.println(hashedPassword); i++; } } }Encryption Result
Environment Setup
1. JDK 8 2. Spring Boot 3. Intellij Idea/ eclipse 4. Mysql DB 4. Maven
Maven Dependencies
spring-boot-starter-parent: provides useful Maven defaults. It also provides a dependency-management section so that you can omit version tags for existing dependencies.
spring-boot-starter-web: includes all the dependencies required to create a web app. This will avoid lining up different spring common project versions.
spring-boot-starter-tomcat: enable an embedded Apache Tomcat 7 instance, by default. We have overriden this by defining our version. This can be also marked as provided if you wish to deploy the war to any other standalone tomcat.
tomcat-embed-jasper: provides support for .jsp file rendering.
spring-boot-starter-security: take care of all the required dependencies related to spring security.
<properties>
<tomcat.version>8.0.3</tomcat.version>
<start-class>spring-boot-example.Application</start-class>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<!--<scope>provided</scope>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbcp</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Spring Bean Configuration
SpringBootServletInitializer enables process used in Servlet 3.0 using web.xml
@SpringBootApplication: This is a convenience annotation that is equivalent to declaring @Configuration,
@EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan.
package com.devglan.config; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.web.SpringBootServletInitializer; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.devglan") @SpringBootApplication public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer { private static ClassapplicationClass = Application.class; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
Other Interesting Posts AES Encryption and Decryption in Java Spring 5 Features and Enhancements Spring Security Hibernate Example with complete JavaConfig Spring Boot Security Redirect after Login with complete JavaConfig Securing REST API with Spring Security Basic Authentication Spring Security with Spring MVC Example Using Spring Boot Spring JMS Activemq Integration with Spring Boot Websocket spring Boot Integration without STOMP with complete JavaConfig Maintaining Spring Session during Websocket Connection Spring MVC Angularjs Integration with complete JavaConfig Spring Hibernate Integration with complete JavaConfig Spring Junit Integration with complete JavaConfig Spring Ehcache Cacheable Example with complete javaConfig Spring Boot Spring MVC Example Spring Boot Thymeleaf Example
Now let us define our main configuration for spring security - SpringSecurityConfig.java.We have defined our passwordEncoder as a spring bean and configured the
package com.devglan.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher; @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Resource(name = "userDetailService") private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.csrf().requireCsrfProtectionMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("**/login")).and().authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/dashboard").hasRole("USER").and().formLogin().defaultSuccessUrl("/dashboard") .loginPage("/login").and().logout().permitAll(); } @Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){ PasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); return encoder; } @Autowired public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder()); } @Override public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception { web.ignoring().antMatchers("/*.css"); web.ignoring().antMatchers("/*.js"); } }
Now let us configure our beans. This is the configuration responsible to integrate spring with hibernate.
@Configuration : It indicates that a class declares one or more @Bean methods and may be processed by the Spring container to generate bean definitions and service requests for those beans at runtime.
@EnableWebMvc: Adding this annotation to an @Configuration class imports the Spring MVC configuration from WebMvcConfigurationSupport.
BeanConfig.javapackage com.devglan.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc; @Configuration @EnableWebMvc @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.devglan") public class BeanConfig { @Bean public LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory() { LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new LocalSessionFactoryBean(); sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource()); sessionFactory.setPackagesToScan(new String[]{"com.devglan.model"}); sessionFactory.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties()); return sessionFactory; } @Bean public DataSource dataSource() { BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"); dataSource.setUsername("root"); dataSource.setPassword("root"); return dataSource; } Properties hibernateProperties() { return new Properties() { { setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "update"); setProperty("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect"); setProperty("hibernate.show_sql", "true"); } }; } }
This is the class which is reponsible to update the spring security context with valid user and the corresponding role.
SpringSecurityConfig.javapackage com.devglan.service.impl; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.devglan.dao.UserDao; import com.devglan.service.UserService; @Component(value = "userDetailService") public class UserDetailServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService, UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userId) throws UsernameNotFoundException { com.devglan.model.UserDetails user = userDao.findUserById(userId); if(user == null){ throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Invalid username or password."); } return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getId(), user.getPassword(), getAuthority()); } private ListgetAuthority() { return Arrays.asList(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER")); } public List getUsers() { return userDao.getUserDetails(); } }
Now let us define our model class.
UserDetails.javapackage com.devglan.model; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table public class UserDetails { @Id @Column @GeneratedValue private long id; @Column private String username; @Column private String name; @Column private String email; @Column private String password; @Column private String address;UserDaoImpl.java
package com.devglan.dao.impl; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.Criteria; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.devglan.dao.UserDao; import com.devglan.model.UserDetails; @Component public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { @Autowired private SessionFactory sessionFactory; public ListUserController.javagetUserDetails() { Criteria criteria = sessionFactory.openSession().createCriteria(UserDetails.class); return criteria.list(); } public UserDetails findUserById(String userId) { UserDetails userDetails = null; Criteria criteria = sessionFactory.openSession().createCriteria(UserDetails.class); criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("id", userId)); List entityList = criteria.list(); if(!entityList.isEmpty()) { userDetails = entityList.get(0); } return userDetails; } }
package com.devglan.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import com.devglan.service.UserService; @Controller public class DashboardController { @Autowired private UserService userService; @RequestMapping(value = "/dashboard", method = RequestMethod.GET) public ModelAndView dashboard() { ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView(); model.addObject("users", userService.getUsers()); model.setViewName("dashboard"); return model; } }
Client Side
Client side codes are also similar to whatever we have defined in the previous post Spring Security with Spring MVC Example Using Spring Boot.All these are available in the source code which you can download a the end of the post below.
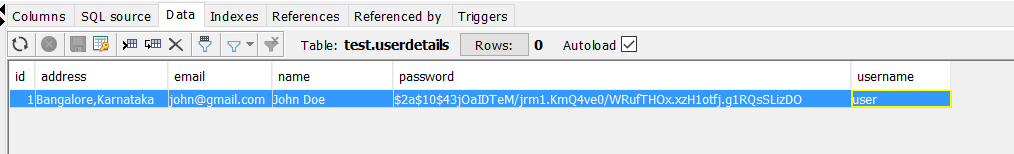
DB Configurations
Following is the screenshot:
Run Application
1. Run Application.java as a java application.
2. Hit the url as http://localhost:8080/ and you will be redirected to /login as below
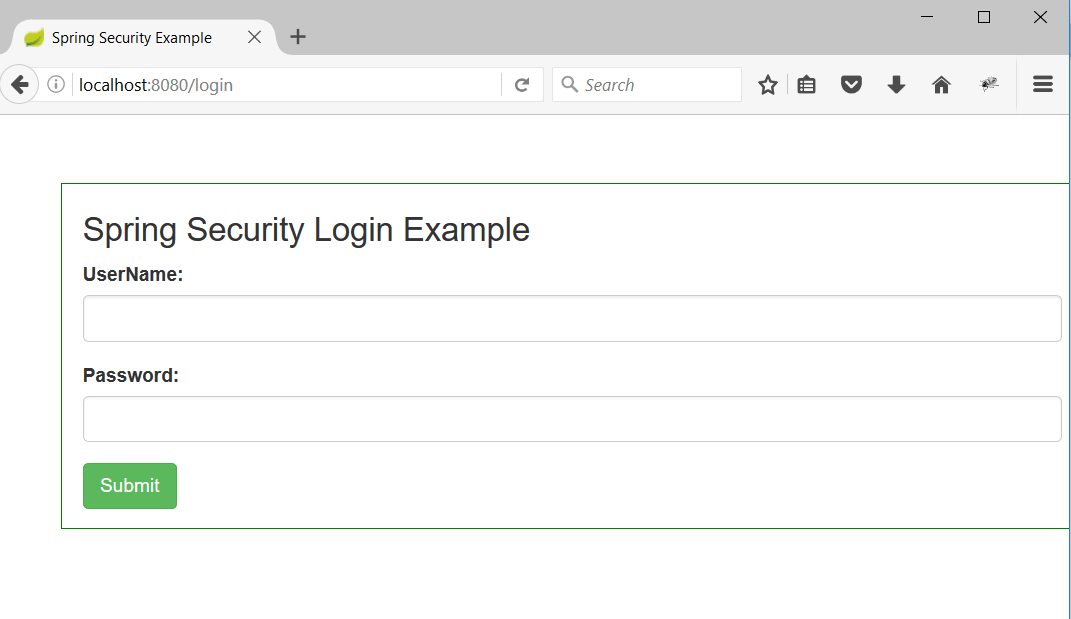
4. Enter the username/password as user/password and hit enter the dashboard page will be rendered.
Conclusion
I hope this article served you that you were looking for. If you have anything that you want to add or share then please share it below in the comment section.