In this post we will be developing a sample spring MVC boot app with embedded tomcat feature provided by Spring boot using maven.Spring boot provides maven artifact spring-boot-starter-tomcatto use embedded tomcat to deploy application.
Background
As we know, spring boot avoids all the boilerplate code and configurations that we generally do while developing a new spring project like adding build path or maven dependencies, configuring application server, adding spring configurations. Spring boot thus helps us use the existing Spring functionalities more robustly and with minimum efforts. Now let us see these use cases by developing a sample spring boot application.
Environment Setup
1. JDK 8 2. Spring Boot 3. Intellij Idea/ eclipse 4. Maven
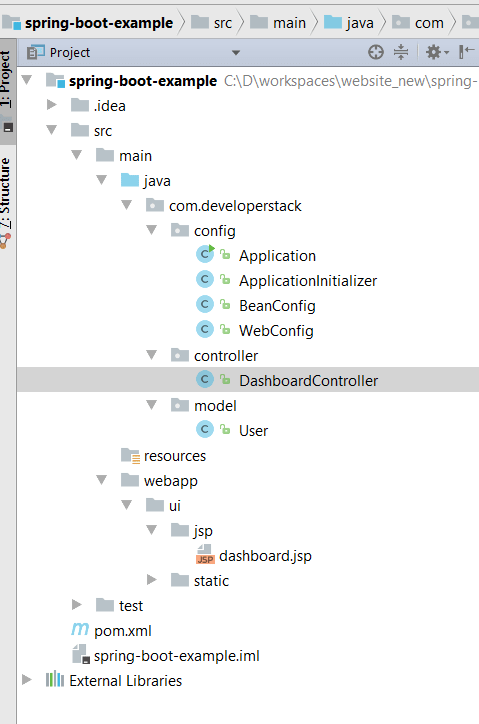
Project Structure
Maven Dependencies
spring-boot-starter-parent: provides useful Maven defaults. It also provides a dependency-management section so that you can omit version tags for existing dependencies.
spring-boot-starter-web: includes all the dependencies required to create a web app. This will avoid lining up different spring common project versions.
spring-boot-starter-tomcat: enable an embedded Apache Tomcat 7 instance, by default. We have overriden this by defining our version. This can be also marked as provided if you wish to deploy the war to any other standalone tomcat.
tomcat-embed-jasper: provides support for .jsp file rendering.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.developerstack</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-example</artifactId> <version>0.1.0</version> <properties> <tomcat.version>8.0.3</tomcat.version> <start-class>spring-boot-example.Application</start-class> </properties> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.3.3.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> <!--<scope>provided</scope>--> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId> <!--<scope>provided</scope>--> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
Spring Bean Configuration
SpringBootServletInitializer enables process used in Servlet 3.0 using web.xml
EnableAutoConfiguration This will help apring boot to automatically identify how to configure Spring, based on the jar dependencies that we have added. Since spring-boot-starter-web added Tomcat and Spring MVC, the auto-configuration will assume that we are developing a web application and setup Spring accordingly.
Application.javapackage com.developerstack.config; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder; import org.springframework.boot.context.web.SpringBootServletInitializer; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.developerstack") @Import({BeanConfig.class, WebConfig.class}) //@EnableWebMvc @EnableAutoConfiguration public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer { private static ClassapplicationClass = Application.class; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } @Override protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) { return application.sources(applicationClass); } }
Other Interesting Posts Spring 5 Features and Enhancements Spring MVC Angularjs Integration with complete JavaConfig Spring Junit Integration with complete JavaConfig Spring Ehcache Cacheable Example with complete javaConfig Spring Boot Thymeleaf Example Spring Boot Security Redirect after Login with complete JavaConfig Spring Security Hibernate Example with complete JavaConfig Securing REST API with Spring Security Basic Authentication Spring Security Password Encoding using Bcrypt Encoder Spring Boot Security Custom Form Login Example Websocket spring Boot Integration Without STOMP with complete JavaConfig Maintaining Spring Session during Websocket Connection
This configuration is responsible to initialize spring based web application. We have implemented WebApplicationInitializer.java to configure the ServletContext programmatically.
ApplicationInitializer.javapackage com.developerstack.config; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration; import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer; import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet; public class ApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer { public void onStartup(ServletContext container) throws ServletException { AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); ctx.setServletContext(container); ServletRegistration.Dynamic servlet = container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(ctx)); servlet.setLoadOnStartup(1); servlet.addMapping("/"); } }BeanConfig.java
package com.developerstack.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView; @Configuration public class BeanConfig { @Bean public InternalResourceViewResolver setupViewResolver() { InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver(); resolver.setPrefix ("/ui/jsp/"); resolver.setSuffix (".jsp"); resolver.setViewClass (JstlView.class); return resolver; } }
By default Spring Boot will serve static content from a directory called /static (or /public or /resources or /META-INF/resources) in the classpath or from the root of the ServletContext. But here we have defined out custom folder structure for static contents, hence it is required to tell Spring boot about how to render static content.
package com.developerstack.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; @Configuration public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void addResourceHandlers(final ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { registry.addResourceHandler("/*.js/**").addResourceLocations("/ui/static/"); registry.addResourceHandler("/*.css/**").addResourceLocations("/ui/static/"); } }
Now let us define our controller that will serve the response to the client. Here we have hardcoded some user details.
DashboardController.javapackage com.developerstack.controller; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import com.developerstack.model.User; @Controller public class DashboardController { @RequestMapping(value = "/dashboard", method = RequestMethod.GET) public ModelAndView dashboard() { ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView(); model.addObject("users", getUsers()); model.setViewName("dashboard"); return model; } private ListgetUsers() { User user = new User(); user.setEmail("johndoe123@gmail.com"); user.setName("John Doe"); user.setAddress("Bangalore, Karnataka"); User user1 = new User(); user1.setEmail("amitsingh@yahoo.com"); user1.setName("Amit Singh"); user1.setAddress("Chennai, Tamilnadu"); User user2 = new User(); user2.setEmail("bipulkumar@gmail.com"); user2.setName("Bipul Kumar"); user2.setAddress("Bangalore, Karnataka"); User user3 = new User(); user3.setEmail("prakashranjan@gmail.com"); user3.setName("Prakash Ranjan"); user3.setAddress("Chennai, Tamilnadu"); return Arrays.asList(user, user1, user2, user3); } }
Now let us define our dashboard.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <html> <head> <title> Spring Boot Example</title> <link href="/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"> <script src="/jquery-2.2.1.min.js"></script> <script src="/bootstrap.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div> <div class="container" style="margin:50px"> <div class="row text-center"><strong> User Details</strong></div> <div class="row" style="border:1px solid green;padding:10px"> <div class="col-md-4 text-center"><strong>Name</strong></div> <div class="col-md-4 text-center"><strong>Email</strong></div> <div class="col-md-4 text-center"><strong>Address</strong></div> </div> <c:forEach var="user" items="${users}"> <div class="row" style="border:1px solid green;padding:10px"> <div class="col-md-4 text-center">${user.name}</div> <div class="col-md-4 text-center" >${user.email}</div> <div class="col-md-4 text-center">${user.address}</div> </div> </c:forEach> </div> </div> </body> </html>
Run Application
There are 2 ways with which we can run this application.
1. Either we can define the scope of spring-boot-starter-tomcat as provided and create a .war file with maven command and deploy it to standalone tomacat.
Or run Application.java as a java application.
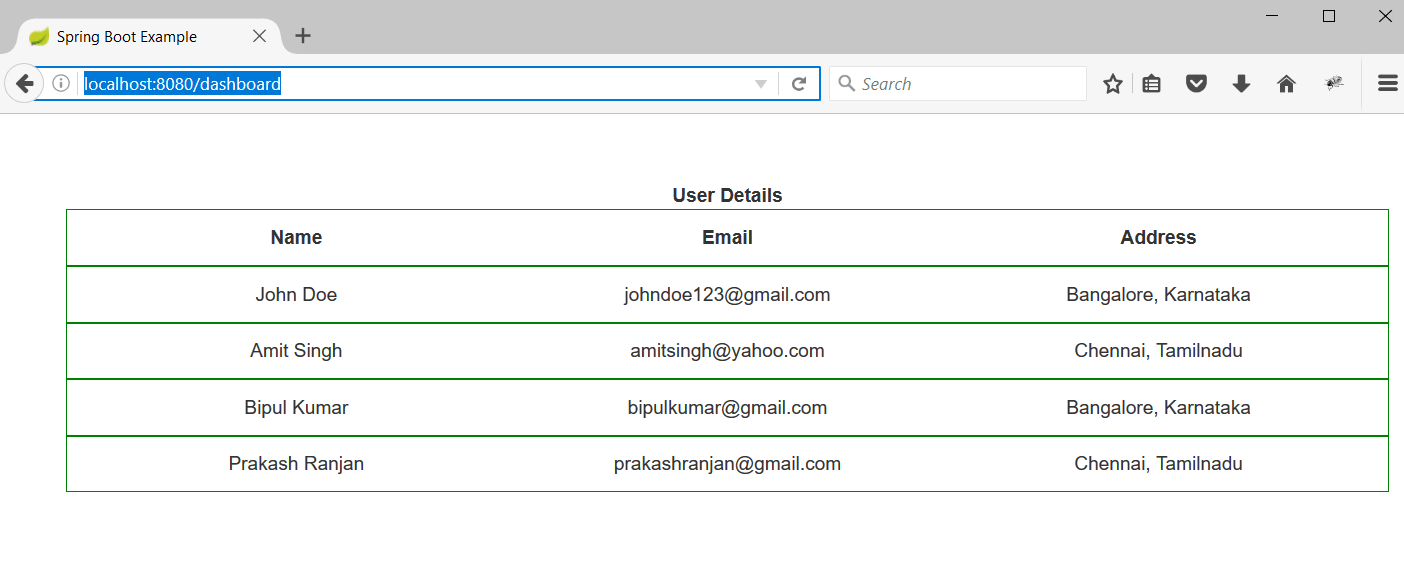
2. Hit the url as http://localhost:8080/dashboard. This will execute the dashboard() method and dashboard.jsp page will be displayed as below:
Conclusion
I hope this article served you that you were looking for. If you have anything that you want to add or share then please share it below in the comment section.